A Single Point of Failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that, if it breaks, stops everything from working. Think of it as the one weak link that can ruin the whole chain. Good system design aims to find and remove these weak links to keep things running smoothly.
Why SPOFs Are a Big Problem
Imagine a system without a SPOF like a team of rowers in a boat. If one rower gets tired, others can keep rowing. But a system with a SPOF is like a boat with one motor—if the motor fails, the boat stops. In tech, SPOFs are a no-go for systems that need to stay online, handle growth, or recover from problems.
Part 1: Spotting SPOFs in a System
SPOFs can hide in different parts of your setup. Here’s where they often show up:
1. Hardware and Infrastructure
- One Server: If your app, database, or logic runs on a single server, it’s a SPOF.
- One Network Device: A single switch or router connecting your system to the internet.
- One Power Source: A single power supply for your servers or data center.
- One Internet Provider: Relying on just one ISP for your connection.
- One Data Center: Hosting everything in a single location.
2. Software and Apps
- One Big App: A single app where one bug can crash everything.
- One Database: A single database server—if it fails, your app can’t access data.
- Session Storage: Storing user data (like login info) on one server, so if it crashes, users get logged out.
3. Data and Storage
- One Hard Drive: Storing data on a single disk with no backup.
- One Main Database: A database setup where only one server handles updates.
4. Third-Party Services
- One Payment Provider: If your only payment service goes down, you can’t process payments.
- One Login Service: Relying on something like “Sign in with Google” for user access.
- One External API: Depending on an outside service you don’t control.
Part 2: How to Get Rid of SPOFs
To eliminate SPOFs, follow these simple ideas:
- Redundancy: Have backup components ready to take over.
- Replication: Keep copies of data in multiple places.
- Independence: Design parts to work on their own, so one failure doesn’t break everything.
- Automation: Use tools to spot problems and fix them without human help.
Part 3: Practical Ways to Fix SPOFs
Here’s how to tackle the SPOFs we listed:
Fixing Hardware and Infrastructure
- Use Multiple Servers:
- Problem: One server fails, and your app stops.
- Solution: Use a load balancer to spread traffic across several servers. If one fails, the others take over.
-
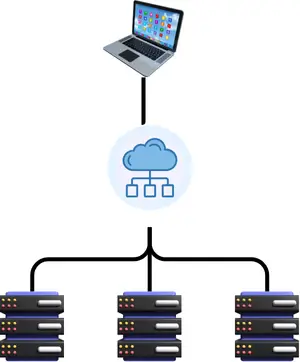
- Spread Across Locations:
- Problem: One data center goes down.
- Solution: Use multiple data centers in the same area (Multi-AZ) or in different regions (Multi-Region) for backup and better performance.
- Use Multiple Networks:
- Problem: One network device or ISP fails.
- Solution: Have backup network devices and use multiple ISPs.
Fixing Data and Databases
- Replicate Databases:
- Problem: One database server crashes.
- Solution: Use a main database for updates and copies for reading. If the main one fails, a copy can take over. Or use databases like DynamoDB or Cassandra, built to avoid SPOFs.
- Use Safe Storage:
- Problem: Data on one disk is lost if it fails.
- Solution: Store data in services like Amazon S3, which automatically makes copies across multiple locations.
Fixing Software and Apps
- Break Up Big Apps:
- Problem: One bug crashes the whole app.
- Solution: Split the app into smaller, independent pieces (microservices). If one piece fails, others keep working.
- Store Sessions Safely:
- Problem: User data stored on one server is lost if it crashes.
- Solution: Save user data in a shared system like Redis, so any server can access it.
- Handle Slow Services:
- Problem: A slow or broken service drags down your system.
- Solution: Use a “circuit breaker” to stop calling a failing service, letting it recover without crashing your app.
Fixing Third-Party Dependencies
- Have Backup Options:
- Problem: Your payment or login service goes down.
- Solution: Use multiple providers (e.g., Stripe and Braintree for payments). If one fails, switch to the other. Offer email login if “Sign in with Google” is down.
- Save External Data:
- Problem: An external API you rely on fails.
- Solution: Store its data in your system. If the API goes down, you can use the saved data, even if it’s slightly old.
Part 4: Example: Building an E-Commerce Platform Without SPOFs
Here’s how to design an online store with no SPOFs:
| Component | SPOF Problem | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Web Servers | One server crashes. | Use multiple servers with a load balancer. |
| Database | Database server fails. | Use a database with a backup in another location. |
| Session Data | Users lose sessions if a server fails. | Store sessions in a shared system like Redis. |
| Product Images | Disk failure loses images. | Store images in Amazon S3 for automatic backups. |
| Payment | Payment provider goes down. | Use multiple payment providers with automatic switching. |
| Data Center | Entire region has an outage. | Use multiple regions and route users to a working one. |
Part 5: How to Find and Fix SPOFs
- Map Your System: Draw a diagram of all parts, big and small.
- Ask “What If?”: For each part, imagine what happens if it fails.
- Rank the Damage: Decide which failures cause the worst problems.
- Focus on Big Risks: Fix the SPOFs that could cause major outages first.
- Add Backups: Use replication, load balancing, or other fixes.
- Test Everything: Regularly test by “breaking” parts (e.g., shutting off a server) to ensure backups work. This is called Chaos Engineering.
Conclusion
Removing SPOFs is a key part of building reliable systems. It’s about planning for failure and making sure your system can keep going. No system is perfect, but with backups, independence, and automation, you can create something strong, reliable, and trustworthy.
Share this article
Test Your Knowledge
Ready to put what you've learned to the test? Take our interactive quiz and see how well you understand the concepts covered in this article.


Loading comments...