Proxies are like middlemen in networking, helping with security, speed, and managing connections. But people often mix up Proxy (Forward Proxy) and Reverse Proxy because they sound similar, even though they do opposite things. Let’s break it down in simple terms with examples and use cases.
What is a Proxy Server?
A Proxy Server (or Forward Proxy) sits between you (the user) and the internet. When you want to visit a website, the proxy gets it for you and sends it back.
How It Works
- You ask to visit a website (like www.example.com).
- The proxy server takes your request.
- It sends the request to the website for you.
- The website sends the data back to the proxy.
- The proxy gives the data to you.
Flow: You → Proxy → Internet
Example
Imagine you’re at school, and social media is blocked. You use a proxy server in another country to access Instagram. The proxy gets Instagram for you, bypassing the school’s restrictions.
Example Path:

Why Use a Proxy?
- Privacy: Hides your real location (IP address).
- Blocking Websites: Stops you from visiting certain sites (like in offices).
- Access Blocked Content: Lets you visit websites that are restricted in your area.
- Faster Browsing: Saves copies of websites to load them quicker next time.
What is a Reverse Proxy?
A Reverse Proxy sits in front of servers, not users. It handles requests from users and decides which server should deal with them. It’s all about protecting and managing the servers.
How It Works
- You visit a website (like www.myapp.com).
- The reverse proxy gets your request.
- It picks the right server to handle it.
- The server sends the data back to the reverse proxy.
- The reverse proxy sends it to you.
Flow: You → Reverse Proxy → Internal Servers
Example
Big websites like Netflix use a reverse proxy to handle millions of users. When you watch a show, your request goes to the reverse proxy (like Nginx), which sends it to one of Netflix’s many servers.
Example Daigram:
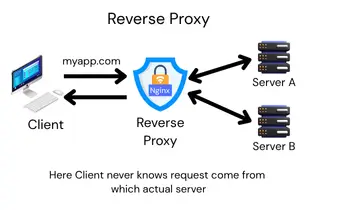
Why Use a Reverse Proxy?
- Security: Hides the real servers from users.
- Load Balancing: Splits traffic across multiple servers to avoid overload.
- Encryption: Manages secure connections (HTTPS).
- Caching: Stores data to make websites load faster.
- Reliability: Keeps things running even if a server fails.
Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy: Quick Comparison
| Feature | Proxy (Forward) | Reverse Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| What It Protects | You (the user) | The server |
| Sits Between | You and the internet | Users and servers |
| Who Starts Request | You | You (but proxy manages server side) |
| Main Job | Privacy, bypassing restrictions | Security, load balancing, speed |
| Examples | Squid, CCProxy | Nginx, HAProxy, Cloudflare |
| Who’s Hidden? | Your identity (from websites) | Server details (from users) |
| Common Use | Offices, VPNs | Websites, apps, CDNs |
Analogy to Understand
- Proxy: Like a personal assistant who runs errands for you without telling anyone it’s you.
- Reverse Proxy: Like a receptionist at a company who directs visitors to the right department without revealing how the company is organized.
Proxy = Protects you.
Reverse Proxy = Protects the server.
Tools for Proxies
Proxy Tools
- Squid: Filters and caches web content.
- CCProxy: Easy proxy for Windows users.
Reverse Proxy Tools
- Nginx: Handles traffic and security for websites.
- HAProxy: High-speed load balancer.
- Cloudflare: Protects and speeds up websites.
Simple Reverse Proxy Example (Nginx)
Here’s how you might set up a reverse proxy with Nginx:
server {
listen 80; # Listen for web requests
server_name myapp.com; # Website name
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5000; # Send requests to this server
proxy_set_header Host $host; # Pass along user info
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}
What This Does:
All requests to myapp.com go to the reverse proxy, which sends them to a server running on port 5000. It keeps the server hidden and secure.
Where Are They Used?
Proxy Server
- Offices to block certain websites.
- People using VPNs for privacy.
- Schools to limit internet access.
- Bypassing blocked websites (e.g., accessing YouTube in a restricted country).
Reverse Proxy
- Big websites like Amazon or YouTube.
- Content delivery networks (CDNs) like Cloudflare.
- Apps with many servers (microservices).
- Balancing traffic for busy websites.
Final Thoughts
- Use a Proxy when you want to hide or protect yourself (the user).
- Use a Reverse Proxy when you want to protect or manage servers.
Both are super important in today’s internet. Proxies keep users private and help bypass restrictions, while reverse proxies make websites fast, secure, and reliable.
Quick Summary
| Type | Protects | Sits Between | Main Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proxy (Forward) | User | User → Internet | Privacy, bypassing blocks |
| Reverse Proxy | Server | Internet → Servers | Security, speed, balancing |
Share this article
Test Your Knowledge
Ready to put what you've learned to the test? Take our interactive quiz and see how well you understand the concepts covered in this article.


Loading comments...